| Optimization Toolbox |   |
Output Headings: Medium-Scale Algorithms
When the options Display parameter is set to 'iter' for fminsearch, fminbnd, fzero, fgoalattain, fmincon, lsqcurvefit, fminunc, fsolve, lsqnonlin, fminimax, and fseminf, output is produced in column format.
fminsearch
For fminsearch, the column headings are
Iteration is the iteration number.
Func-count is the number of function evaluations.
min f(x) is the minimum function value in the current simplex.
Procedure gives the current simplex operation: initial, expand, reflect, shrink, contract inside, and contract outside.
fzero and fminbnd
For fzero and fminbnd, the column headings are
Func-count is the number of function evaluations (which for fzero is the same as the number of iterations).
x is the current point.
f(x) is the current function value at x.
Procedure gives the current operation. For fzero, these include initial (initial point), search (search for an interval containing a zero), bisection (bisection search), and interpolation. For fminbnd, the possible operations are initial, golden (golden section search), and parabolic (parabolic interpolation).
fminunc
For fminunc, the column headings are
Iteration is the iteration number.
Func-count is the number of function evaluations.
f(x) is the current function value.
Step-size is the step size in the current search direction.
Directional derivative is the gradient of the function along the search direction.
lsqnonlin and lsqcurvefit
For lsqnonlin and lsqcurvefit, the headings are
where Iteration, Func-count, Step-size, and Directional derivative are the same as for fminunc, and
Residual is the residual (sum of squares) of the function.
Lambda is the 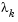 value defined in Least-Squares Optimization. (This value is displayed when you use the Levenberg-Marquardt method and omitted when you use the Gauss-Newton method.)
value defined in Least-Squares Optimization. (This value is displayed when you use the Levenberg-Marquardt method and omitted when you use the Gauss-Newton method.)
fsolve
For fsolve with the default trust-region dogleg method, the headings are
Iteration is the iteration number.
Func-count is the number of function evaluations.
f(x) is the sum of squares of the current function value.
Norm of step is the norm of the current step size.
First-order optimality is the infinity norm of the current gradient.
Trust-region radius is the radius of the trust region for that step.
For fsolve with either the Levenberg-Marquardt or Gauss-Newton method, the headings are
Residual is the residual (sum of squares) of the function.
Step-size is the step-size in the current search direction.
Directional derivative is the gradient of the function along the search direction.
fmincon and fseminf
For fmincon and fseminf, the headings are
Iter is the iteration number.
F-count is the number of function evaluations.
f(x) is the current function value.
Directional derivative is the gradient of the function along the search direction.
Procedure gives a message about the Hessian update and QP subproblem.
The Procedure messages are discussed in Updating the Hessian Matrix.
For fgoalattain and fminimax, the headings are the same as for fmincon except that f(x) and max constraint are combined into Max{F,constraints}. Max{F,constraints} gives the maximum goal violation or constraint violation for fgoalattain and the maximum function value or constraint violation for fminimax.
 | Displaying Iterative Output | Output Headings: Large-Scale Algorithms |  |