

| System Identification Toolbox |   |
Plot frequency functions in Bode diagram form.
Syntax
bode(m) [mag,phase,w] = bode(m) [mag,phase,w,sdmag,sdphase] = bode(m) bode(m1,m2,m3,...,w) bode(m1,'PlotStyle1',m2,'PlotStyle2',...) bode(m1,m2,m3,..'sd',sd,'mode',mode,'ap',ap)
bode(m1,m2,m3,..'sd',sd,'mode',mode,'ap',ap,'fill')
Description
bode computes the magnitude and phase of the frequency response of idmodel and idfrd models. When invoked without left-hand arguments, bode produces a Bode plot on the screen.
bode(m) plots the Bode response of an arbitrary idmodel or idfrd model m. This model can be continuous or discrete, and SISO or MIMO. The InputNames and OuputNames of the models are used to plot the responses for different I/O channels in separate plots. Pressing the Enter key advances the plot from one input-output pair to the next one.
If m contains information about both I/O channels and output noise spectra, only the I/O channels are shown. To show the output noise spectra enter m('n') ('n' for 'noise') in the model list. Analogously, specific I/O channels can be selected by the normal subreferencing: m(ky,ku).
Arguments sd, ap, mode and w
The arguments sd, ap, mode and w can appear in any order, or be omitted.
sd: If sd is specified as a number larger than zero, confidence intervals for the functions are added to the graph as dash-dotted curves (of the same color as the estimate curve). They indicate the confidence regions corresponding to sd standard deviations. If an argument 'fill' is included in the argument list, the confidence region is marked as a filled band instead.
ap: By default, amplitude and phase plots are shown simultaneously for each I/O channel present in m. For spectra, phase plots are omitted. To show amplitude plots only, use 'ap'= 'A'. For phase plots only, use 'ap'= 'P'. The default is 'ap' = 'B' for both plots.
mode: To obtain all plots on the same diagram use mode = 'same'.
w: bode(m,w) explicitly specifies the frequency range or frequency points to be used for the plot or for computing the response. To focus on a particular frequency interval [wmin,wmax], set w = {wmin,wmax} (Notice the curly brackets). To use particular frequency points, set w to the vector of desired frequencies. Use logspace to generate logarithmically spaced frequency vectors. All frequencies should be specified in radians/sec.
Note that the frequencies cannot be specified for idfrd objects. For those the plot and response are calculated for the internally stored frequencies.
Several Models
bode(m1,m2,...,mN) or bode(m1,m2,...mN,w) plots the Bode response of several idmodel or idfrd models on a single figure. The models may be mixes of different sizes and continuous/discrete. The sorting of the plots is made based on the InputNames and OutputNames. If the frequencies w are specified, these will apply to all non-idfrd models in the list. If you want different frequencies for different models, you should thus first convert them to idfrd objects using the idfrd command.
bode(m1,'PlotStyle1',...,mN,'PlotStyleN') further specifies which color, linestyle and/or marker should be used to plot each system, as in
Arguments
The output argument w contains the frequencies for which the response is given, whether specified among the input arguments or not. The output arguments mag and phase are 3-D arrays with dimensions
For SISO systems mag(1,1,k) and phase(1,1,k) give the magnitude and phase (in degrees) at the frequency 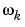
= w(k). To obtain the result as a normal vector of responses use mag = mag(:) and phase = phase(:).
For MIMO systems mag(i,j,k) is the magnitude of the frequency response at frequency w(k) from input j to output i, and similairly for phase(i,j,k).
If sdmag and sdphase are specified, the standard deviations of the magnitude and phase are also computed. Then sdmag is an array of the same size as mag, containing the estimated standard deviations of the response, and analogously for sdphase.
See Also
etfe, ffplot, freqresp, idfrd, nyquist, spa
 | bj | compare |  |