

| System Identification Toolbox |   |
Estimate recursively the parameters of an Output-Error model.
Syntax
Description
The parameters of the Output-Error model structure
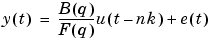
are estimated using a recursive prediction error method.
The input-output data are contained in z, which is either an iddata object or a matrix z = [y u] where y and u are column vectors. nn is given as
where nb and nf are the orders of the Output-Error model, and nk is the delay. Specifically,
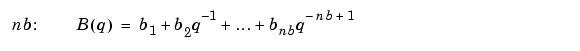
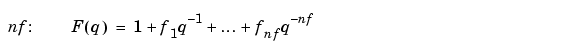
See Polynomial Representation of Transfer Functions in the "Tutorial" for more information.
Only single-input, single-output models are handled by roe. Use rpem for the multi-input case.
The estimated parameters are returned in the matrix thm. The k-th row of thm contains the parameters associated with time k, i.e., they are based on the data in the rows up to and including row k in z.
Each row of thm contains the estimated parameters in the following order.
yhat is the predicted value of the output, according to the current model, i.e., row k of yhat contains the predicted value of y(k) based on all past data.
The actual algorithm is selected with the two arguments adg and adm. These are described under rarx.
The input argument th0 contains the initial value of the parameters, a row vector, consistent with the rows of thm. (See above.) The default value of th0 is all zeros.
The arguments P0 and P are the initial and final values, respectively, of the scaled covariance matrix of the parameters. See rarx. The default value of P0 is 104 times the unit matrix. The arguments phi0, psi0, phi, and psi contain initial and final values of the data vector and the gradient vector, respectively. The sizes of these depend in a rather complicated way on the chosen model orders. The normal choice of phi0 and psi0 is to use the outputs from a previous call to roe with the same model orders. (This call could be a dummy call with default input arguments.) The default values of phi0 and psi0 are all zeros.
Note that the function requires that the delay nk is larger than 0. If you want nk=0, shift the input sequence appropriately and use nk=1.
Algorithm
The general recursive prediction error algorithm (11.44) of Ljung (1999) is implemented. See also Recursive Parameter Estimation in the "Tutorial"
See Also
oe, rarx, rbj, rplr, rpem, nkshift
 | resid | rpem |  |