

| System Identification Toolbox |   |
Compute fit between simulated and measured output for a group of model structures.
Syntax
Description
NN is a matrix that defines a number of different structures of the ARX type. Each row of NN is of the form
with the same interpretation as described for arx. See struc for easy generation of typical NN matrices for single-input systems.
Each of ze and zv are iddata objects containing output-input data. Models for each model structure defined in NN are estimated using the instrumental variable (IV) method on data set ze. The estimated models are simulated using the inputs from data set zv. The normalized quadratic fit between the simulated output and the measured output in zv is formed and returned in v. The rows below the first row in v are the transpose of NN, and the last row contains the logarithms of the condition numbers of the IV matrix
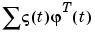
A large condition number indicates that the structure is of unnecessarily high order (see page 498 in Ljung (1999)).
The information in v is best analyzed using selstruc.
If p is equal to zero, the computation of condition numbers is suppressed. For the use of maxsize, see Algorithm Properties.
The routine is for single-output systems only.
Note
The IV method used does not guarantee that the obtained models are stable. The output-error fit calculated in v may then be misleading.
|
Examples
Compare the effect of different orders and delays, using the same data set for both the estimation and validation.
Algorithm
A maximum order ARX model is computed using the least-squares method. Instruments are generated by filtering the input(s) through this model. The models are subsequently obtained by operating on submatrices in the corresponding large IV matrix.
See Also
arxstruc, iv4, n4sid, selstruc, struc
 | ivar | ivx |  |