

| System Identification Toolbox |   |
Package a greybox model structure defined by a user-written M-file into an idgrey model.
Syntax
m = idgrey(MfileName,ParameterVector,CDmfile) m = idgrey(MfileName,ParameterVector,CDmfile,FileArgument,Ts,... 'Property1',Value1,...,'PropertyN',ValueN)
Description
The function idgrey is used to create arbitrarily parameterized state-space models as idgrey objects.
MfileName is the name of an M-file that defines how the state-space matrices depend on the parameters to be estimated. The format of this M-file is given by
and is further discussed below.
ParameterVector is a column vector of the nominal/initial parameters. Its length must be equal to the number of free parameters in the model (that is, the argument pars in the example below).
The argument CDmfile describes how the user-written M-file handles continuous/discrete-time model. It takes the following values:
CDmfile = 'cd': The M-file returns the continuous-time state-space matrices when called with the argument Tsm=0. When called with a value Tsm>0 the M-file returns the discrete-time state-space matrices, obtained by sampling the continuous-time system with sampling interval Tsm. The M-file must consequently in this case include the sampling procedure.
CDmfile = 'c'. The M-file always returns the continuous-time state-space matrices, no matter the value of Tsm. In this case the toolbox's estimation routines will provide the sampling when fitting the model to discrete-time data.
CDmfile='d'. The M-file always returns discrete-time state-space matrices, that may or may not depend on Tsm.
The argument FileArgument corresponds to the auxiliary argument Auxarg in the user-written M-file. It can be used to handle several variants of the model structure, without having to edit the M-file. If it is not used, enter FileArgument = []. (Default).
Ts denotes the sampling interval of the model. Its default value is Ts = 0, that is, a continuous-time model.
The idgrey object is a child of idmodel. Therefore any idmodel properties can be set as property name/property value pairs in the idgrey command. They can of course also be set by the command set, or by subassignment, like
There are also two properties, DisturbanceModel and InitialState that can be used to affect the parameterizations of K and X0, thus overriding the outputs from the M-file. See below.
idgrey Properties
To summarize, the properties of idgrey are the following ones:
MfileName: The name of the user-written M-file. See below for details
CDmfile: How this file handles continuous/discrete models, depending on its second argument T.
CDmfile = 'cd' means that the mfile returns the continuous time state space model matrices when the argument T = 0, and the discrete time model, obtained by sampling with sampling interval T when T > 0.
CDmfile= 'c' means that the mfile always returns continuous time model matrices, no matter the value of T.
CDmfile = 'd' means that the mfile always returns discrete time model matrices that may or may not depend on the value of T.
FileArgument: Possible extra input arguments to the user-written M-file
DisturbanceModel: affects the parameterization of the K-matrix. It can assume the following values:
'Model': This is the default. It means that the K matrix obtained from the user-written M-file is used.
'Estimate': The K-matrix is treated as unknown and its elements are estimated as free parameters.
'Fixed': The K-matrix is fixed to a given value.
'Zero': The K-matrix is fixed to zero, thus producing an output error model.
K from the user written M-file is ignored. The estimated/fixed value is stored internally and does not change when the model is sampled/resampled/or converted to continuous time. Note also that this estimated value is tailored only to the sampling interval of the data.
InitialState: affects the parameterization of the X0-vector. It assumes the same values as DisturbanceModel, with analogous interpretations. In addition InitialState can assume the value `Backcast', with the same interpretation as for an idss object.
A, B, C, D, K, and X0: The state-space matrices. For idgrey models only 'K' and 'X0' can be set, the others only retrieved. The set 'K' and 'X0' are relevant only when DisturbanceModel/InitialState are Estimate or Fixed.
dA, dB, dC, dD, dK, and dX0: The estimated standard deviations of the state-space matrices. These cannot be set, only retrieved.
In addition, any idgrey object also has all the properties of idmodel. See Algorithm Properties and the reference page for idmodel.
Note that all properties can be set/get either by these commands or by subscripts. Autofill applies to all properties and values, and are case insensitive.
For a complete list of property values, use get(m). To see possible value assignments, use set(m). See also idprops and idgrey.
M-File Details
The model structure corresponds to the general linear state-space structure
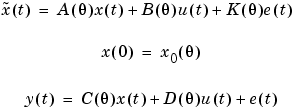
Here 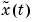 is the time derivative
is the time derivative 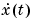 for a continuous time model and
for a continuous time model and 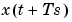 for a discrete time model.
for a discrete time model.
The matrices in this time-discrete model can be parameterized in an arbitrary way by the vector 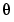 . Write the format for the M-file as follows.
. Write the format for the M-file as follows.
Here the vector pars contains the parameters 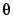 , and the output arguments
, and the output arguments A, B, C, D, K, and x0 are the matrices in the model description that correspond to this value of the parameters and this value of the sampling interval T.
T is the sampling interval, and Auxarg is any variable of auxiliary variables with which you want to work. (In that way you can change certain constants and other aspects in the model structure without having to edit the M-file.) Note that the two arguments T and Auxarg must be included in the function head of the M-file, even if they are not utilized within the M-file.
Section State-Space Models with Coupled Parameters: the idgrey Model of the "Tutorial" contains several examples of typical M-files that define model structures.
A comment about CDmfile: If a continuous time model is sought, it is of course most easy to let the mfile deliver just the continuous time model, i.e., have CDmfile = 'c', and rely upon the toolbox's routines for the proper sampling. Similarly, if the underlying parameterization is indeed discrete time, it is natural to deliver the discrete time model matrices, and let CDmfile = 'd'. If the underlying parameterization is continuous, but you prefer for some reason to do your own sampling inside the mfile, in accordance with the value of T, then it is preferable to let your mfile deliver the continuous time model when called with T = 0, that is, the alternative CMmfile = 'cd'. This will avoid sampling, and then transforming back (using d2c) to find the continuous time model.
Examples
Use the M-file 'mynoise' given in Example 3.4: Parametrized Disturbance Models in the of the "Tutorial" to obtain a physical parametrization of the Kalman gain.
 | idfrd | idinput |  |