

| System Identification Toolbox |   |
Transform the model objects of the System Identification Toolbox to the LTI models of the Control System Toolbox.
Syntax
Description
mod is any idmodel object: idgrey, idarx, idpoly, idss, idmodel, or idfrd. However, idfrd objects can only be converted to frd objects.
sys is returned as the indicated LTI model. The noise input channels in mod are treated as follows.
Consider a model mod with both measured input channels u (nu channels) and noise channels e (ny channels) with covariance matrix 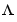
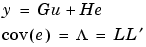
where L is a lower triangular matrix. Note that mod.NoiseVariance = 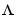 . The model can also be described with unit variance, normalized noise source v.
. The model can also be described with unit variance, normalized noise source v.
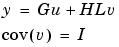
For ss, tf, and zpk, both measured input channels u and normalized noise input channels v in mod will be input channels in sys. The noise input channels will belong to the InputGroup 'Noise', while the others belong to the InputGroup 'Measured'. The names of the noise input channels will be v@yname, where yname is the name of the corresponding output channel. This means that the LTI object realizes the transfer function [G HL].
For frd, no noise input information is included.
To transform only the measured input channels in sys, use
and analogously for tf and zpk. This will give a representation of just G.
For a time series, (no measured input channels, nu = 0), the LTI representations in ss, tf, zpk, and frd contain the transfer functions from the normalized noise sources v to the outputs., that is HL. If the model m has both measured and noise inputs, sys = ss(mod('n')) will give a representation of the additive noise. For frd no output is given for a time-series model.
In addition, the normal subreferencing can be used.
If you want to describe [G H] or H (unnormalized noise), from e to y, use first
to convert the noise channels e to regular input channels. These channels will have the names e@yname.
 | spa | ssdata |  |