

| System Identification Toolbox |   |
Direct Estimation of the Impulse Response
A linear system can be described by the impulse response 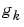 , with the property that
, with the property that
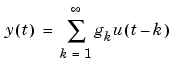
The name derives from the fact that if the input u(t) is an impulse, i.e., u(t)=1 when t=0 and 0 when t>0, then the output y(t) will be 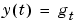 . For a multivariable system, the impulse response
. For a multivariable system, the impulse response 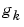 will be a ny-by-nu matrix, where ny is the number of outputs and nu is the number of inputs. Its i-j element thus describes the behavior of the i-th output after an impulse in the j-th input.
will be a ny-by-nu matrix, where ny is the number of outputs and nu is the number of inputs. Its i-j element thus describes the behavior of the i-th output after an impulse in the j-th input.
By choosing menu item Estimate > Correlation Model impulse response coefficients are estimated directly from the input/output data using so called correlation analysis. The actual method is described under the command impulse in the "Command Reference" chapter. For a quick action, you can also just type the letter c in the ident window. This is the hotkey for correlation analysis.
The resulting impulse response estimate is placed in the Model Board, under the default name imp. (The name can be changed by double-clicking on the model icon and then typing in the desired name in the dialog box that opens.)
The best way to examine the result is to select the Model View Transient
Response. This gives a graph of the estimated response. This view offers a choice between displaying the Impulse or the Step response. For a multivariable system, the different channels, i.e., the responses from a certain input to a certain output, are selected under menu item Channel.
The number of lags for which the impulse response is estimated, i.e., the length of the estimated response, is determined as one of the options in the Transient Response view.
 | Estimating Models | Direct Estimation of the Frequency Response |  |