

| Function Reference |   |
Balance state-space models using a diagonal similarity transformation
Syntax
Description
Given a state-space model sys with matrices 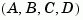 ,
,
computes a diagonal similarity transformation 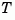 and a scalar
and a scalar 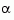 such that
such that
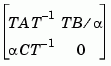
has approximately equal row and column norms. ssbal returns the balanced model sysb with matrices
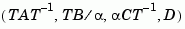
and the state transformation 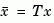 where
where 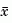 is the new state.
is the new state.
[sysb,T] = ssbal(sys,condT)
specifies an upper bound condT on the condition number of 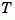 . Since balancing with ill-conditioned
. Since balancing with ill-conditioned 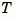 can inadvertently magnify rounding errors,
can inadvertently magnify rounding errors, condT gives control over the worst-case roundoff amplification factor. The default value is condT=Inf.
ssbal returns an error if the state-space model sys has varying state dimensions.
Example
Consider the continuous-time state-space model with the following data.
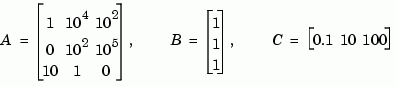
Balance this model with ssbal by typing
ssbal(sys)
a =
x1 x2 x3
x1 1 2500 0.39063
x2 0 100 1562.5
x3 2560 64 0
b =
u1
x1 0.125
x2 0.5
x3 32
c =
x1 x2 x3
y1 0.8 20 3.125
d =
u1
y1 0
Continuous-time system.
Direct inspection shows that the range of numerical values has been compressed by a factor 100 and that the 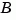 and
and 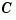 matrices now have nearly equal norms.
matrices now have nearly equal norms.
Algorithm
ssbal uses the MATLAB function balance to compute 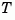 and
and 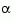 .
.
See Also
balreal
ss2ss
 | ss2ss | ssdata |  |