

| Function Reference |   |
Compute the poles of an LTI system
Syntax
Description
pole
computes the poles p of the SISO or MIMO LTI model sys.
Algorithm
For state-space models, the poles are the eigenvalues of the 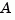 matrix, or the generalized eigenvalues of
matrix, or the generalized eigenvalues of 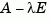 in the descriptor case.
in the descriptor case.
For SISO transfer functions or zero-pole-gain models, the poles are simply the denominator roots (see roots).
For MIMO transfer functions (or zero-pole-gain models), the poles are computed as the union of the poles for each SISO entry. If some columns or rows have a common denominator, the roots of this denominator are counted only once.
Limitations
Multiple poles are numerically sensitive and cannot be computed to high accuracy. A pole 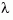 with multiplicity
with multiplicity 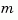 typically gives rise to a cluster of computed poles distributed on a circle with center
typically gives rise to a cluster of computed poles distributed on a circle with center 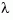 and radius of order
and radius of order
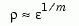
where 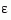 is the relative machine precision (
is the relative machine precision (eps).
See Also
damp
esort, dsort
pzmap
zero
 | place | pzmap |  |