

| Function Reference |   |
Compute damping factors and natural frequencies
Syntax
Description
damp calculates the damping factor and natural frequencies of the poles of an LTI model sys. When invoked without lefthand arguments, a table of the eigenvalues in increasing frequency, along with their damping factors and natural frequencies, is displayed on the screen.
[Wn,Z] = damp(sys) returns column vectors Wn and Z containing the natural frequencies 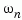 and damping factors
and damping factors 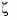 of the poles of
of the poles of sys. For discrete-time systems with poles 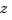 and sample time
and sample time 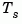 ,
, damp computes "equivalent" continuous-time poles 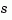 by solving
by solving
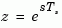
The values Wn and Z are then relative to the continuous-time poles 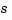 . Both
. Both Wn and Z are empty if the sample time is unspecified.
[Wn,Z,P] = damp(sys) returns an additional vector P containing the (true) poles of sys. Note that P returns the same values as pole(sys) (up to reordering).
Example
Compute and display the eigenvalues, natural frequencies, and damping factors of the continuous transfer function
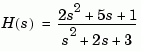
Eigenvalue Damping Freq. (rad/s) -1.00e+000 + 1.41e+000i 5.77e-001 1.73e+000 -1.00e+000 - 1.41e+000i 5.77e-001 1.73e+000
See Also
eig Calculate eigenvalues and eigenvectors
pole
pzmap
zero
 | d2d | dare |  |