

| Function Reference |   |
Form state estimator given estimator gain
Syntax
Description
est = estim(sys,L)
produces a state/output estimator est given the plant state-space model sys and the estimator gain L. All inputs 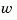 of
of sys are assumed stochastic (process and/or measurement noise), and all outputs 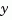 are measured. The estimator
are measured. The estimator est is returned in state-space form (SS object). For a continuous-time plant sys with equations
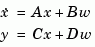
estim generates plant output and state estimates 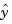 and
and 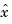 as given by the following model.
as given by the following model.
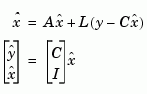
The discrete-time estimator has similar equations.
est = estim(sys,L,sensors,known)
handles more general plants sys with both known inputs 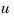 and stochastic inputs
and stochastic inputs 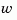 , and both measured outputs
, and both measured outputs 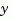 and nonmeasured outputs
and nonmeasured outputs 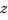 .
.
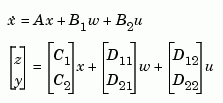
The index vectors sensors and known specify which outputs 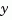 are measured and which inputs
are measured and which inputs 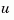 are known. The resulting estimator
are known. The resulting estimator est uses both 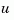 and
and 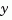 to produce the output and state estimates.
to produce the output and state estimates.
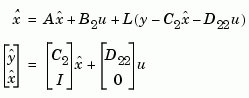
estim handles both continuous- and discrete-time cases. You can use the functions place (pole placement) or kalman (Kalman filtering) to design an adequate estimator gain 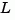 . Note that the estimator poles (eigenvalues of
. Note that the estimator poles (eigenvalues of 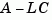 ) should be faster than the plant dynamics (eigenvalues of
) should be faster than the plant dynamics (eigenvalues of 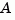 ) to ensure accurate estimation.
) to ensure accurate estimation.
Example
Consider a state-space model sys with seven outputs and four inputs. Suppose you designed a Kalman gain matrix 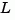 using outputs 4, 7, and 1 of the plant as sensor measurements, and inputs 1,4, and 3 of the plant as known (deterministic) inputs. You can then form the Kalman estimator by
using outputs 4, 7, and 1 of the plant as sensor measurements, and inputs 1,4, and 3 of the plant as known (deterministic) inputs. You can then form the Kalman estimator by
See the function kalman for direct Kalman estimator design.
See Also
kalman
place
reg
 | esort | evalfr |  |