

| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Note
The nnls function was replaced by lsqnonneg in Release 11 (MATLAB 5.3). In Release 12 (MATLAB 6.0), nnls displays a warning message and calls lsqnonneg.
|
Syntax
Description
x = nnls(A,b)
solves the system of equations 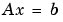 in a least squares sense, subject to the constraint that the solution vector
in a least squares sense, subject to the constraint that the solution vector x has nonnegative elements 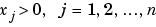 . The solution
. The solution x minimizes 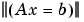 subject to
subject to x >= 0.
x = nnls(A,b,tol)
solves the system of equations, and specifies a tolerance tol. By default, tol is: max(size(A))*norm(A,1)*eps.
[x,w] = nnls(A,b)
also returns the dual vector w, where 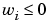 when
when 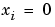 and
and 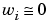 when
when 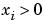 .
.
[x,w] = nnls(A,b,tol)
solves the system of equations, returns the dual vector w, and specifies a tolerance tol.
Examples
Compare the unconstrained least squares solution to the nnls solution for a 4-by-2 problem:
A =0.03720.28690.68610.70710.62330.62450.63440.6170 b =0.85870.17810.07470.8405 [A\bnnls(A,b)]= -2.562703.11080.6929 [norm(A*(a\b)-b)norm(A*nnls(a,b)-b)]=0.66740.9118
The solution from nnls does not fit as well, but has no negative components.
Algorithm
The nnls function uses the algorithm described in [1], Chapter 23. The algorithm starts with a set of possible basis vectors, computes the associated dual vector w, and selects the basis vector corresponding to the maximum value in w to swap out of the basis in exchange for another possible candidate, until w <= 0.
See Also
\ Matrix left division (backslash)
References
[1] Lawson, C. L. and R. J. Hanson, Solving Least Squares Problems,
Prentice-Hall, 1974, Chapter 23.
 | nextpow2 | nnz |  |