

| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Minimize a function of one variable
Note
The fmin function was replaced by fminbnd in Release 11 (MATLAB 5.3). In Release 12 (MATLAB 6.0), fmin displays a warning message and calls fminbnd.
|
Syntax
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2) x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options) x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options,P1,P2, ...) [x,options] = fmin(...)
Description
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2)
returns a value of x which is a local minimizer of fun(x) in the interval 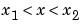 .
.
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options)
does the same as the above, but uses options control parameters.
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options,P1,P2,...)
fun(x,P1,P2,...). Pass an empty matrix for options to use the default value.
[x,options] = fmin(...)
returns, in options(10), a count of the number of steps taken.
Arguments
Examples
fmin('cos',3,4) computes 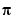 to a few decimal places.
to a few decimal places.
fmin('cos',3,4,[1,1.e-12]) displays the steps taken to compute 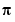 to 12 decimal places.
to 12 decimal places.
To find the minimum of the function 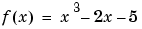 on the interval (0
on the interval (0,2), write an M-file called f.m.
The value of the function at the minimum is
Algorithm
The algorithm is based on golden section search and parabolic interpolation. A Fortran program implementing the same algorithms is given in [1].
See Also
fmins, fzero, foptions in the Optimization Toolbox (or type help foptions).
References
[1] Forsythe, G. E., M. A. Malcolm, and C. B. Moler, Computer Methods for Mathematical Computations, Prentice-Hall, 1976.
 | flow | fminbnd |  |