| Simulink Reference |
  |
Rate Transition
Handles transfer of data between blocks operating at different rates.
Library
Signal Attributes
Description
Transfers data from the output of a block operating at one rate to the input of another block operating at a different rate. The Rate Transition block's parameters allows you to specify options that trade data integrity and deterministic transfer for faster response and/or lower memory requirements.
| Note
See Data Transfer Problems in the online Real-Time Workshop documentation for a discussion of data integrity and deterministic data transfer.
|
In particular, the block supports the following options:
- Deterministic transfer of data with data integrity between blocks operating at different speeds at the cost of maximum latency of data transfer This is the default option.
- Nondeterministic data transfer with minimum latency and assured data integrity but increased memory requirements
- To specify this option, check the Ensure data integrity during data transfer parameter and uncheck the Ensure deterministic data transfer parameter.
- Minimum latency and target size at the cost of nondeterministic data transfer and possible loss of data integrity
- To specify this option, uncheck the Ensure data integrity during data transfer and Ensure deterministic data transfer parameters.
See Sample Rate Transitions in the online Real-Time Workshop documentation for more information.
| Note
The Zero-Order Hold and Unit Delay blocks also enable transfer of data between blocks operating at different rates. However, you should use the Rate Transition block for this purpose because it is designed specifically for this purpose, offers a wider range of options, and is easier to use.
|
Data Type Support
A Rate Transition block accepts and outputs signals of any data type, including fixed-point data types, except int64 and uint64.
Parameters and Dialog Box
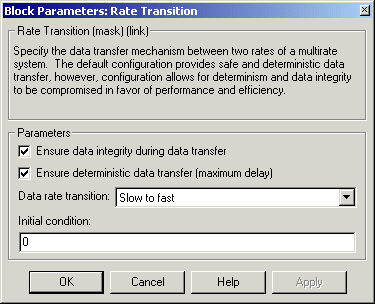
- Ensure data integrity during data transfer
- Selecting this option results in generation of code that ensures the integrity of data transferred by the Rate Transition block. If this option is selected and the transfer is nondeterministic (see Ensure deterministic data transfer option below), the generated code uses double-buffering to prevent the fast block from interrupting the data transfer. Otherwise the generated code uses a copy operation to effect the data transfer. The copy operation consumes less memory than double-buffering but is also interruptible and hence can lead to loss of data during nondeterministic data transfers. Thus, you should select this option if you want the generated code to operate both with maximum responsiveness (i.e., nondeterministically) and assured data integrity. See Rate Transition Block Options in the online Real-Time Workshop documentation for more information.
- Ensure deterministic data transfer (maximum delay)
- Selecting this option causes code generation to generate code that transfers data at the sample rate of the slower block, i.e., deterministically. If this option is not selected, data transfers occur as soon as new data is available from the source block and the receiving block is ready to receive the data. This avoids the need to delay transfers, thus ensuring that the system operates with maximum responsiveness. However, it also means that transfers can occur unpredictably, which is undesirable in some applications. See Rate Transition Block Options in the online Real-Time Workshop documentation for more information.
- Data rate transition
- Select
Slow to fast if the block connected to the input of the Rate Transition block operates at a slower rate than the block connected to the Rate Transition block. Otherwise, select Fast to slow.
- Initial condition
- This parameter applies only to
Slow to fast transitions. It specifies the Rate Transition's initial output at the beginning of a transition when there is not yet any output from the slow block connected to the Rate Transition block's input.
Characteristics
Direct Feedthrough
|
No for slow-to-fast transitions that are protected, i.e., for which you have checked the Ensure data integrity during data transfer option; otherwise, yes.
|
Sample Time
|
This block supports discrete-to-discrete and discrete-to-continuous transitions.
|
Scalar Expansion
|
Of input.
|
Dimensionalized
|
Yes
|
Zero Crossing
|
No
|
 | Rate Limiter | | Real-Imag to Complex |  |






