

| Image Processing Toolbox |   |
Distinct Block Operations
Distinct blocks are rectangular partitions that divide a matrix into m-by-n sections. Distinct blocks overlay the image matrix starting in the upper-left corner, with no overlap. If the blocks don't fit exactly over the image, the toolbox adds zero padding so that they do. Figure 6-3 shows a 15-by-30 matrix divided into 4-by-8 blocks.
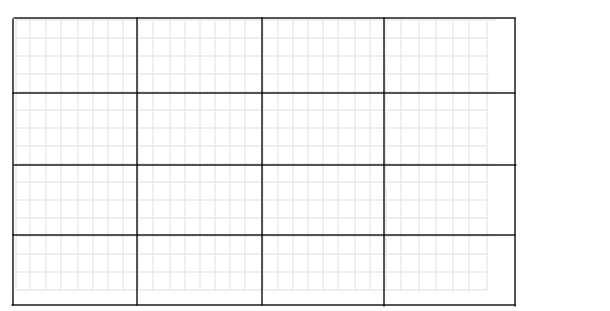
Figure 6-3: An Image Divided into Distinct Blocks
The zero padding process adds 0's to the bottom and right of the image matrix, as needed. After zero padding, the matrix is size 16-by-32.
The function blkproc performs distinct block operations. blkproc extracts each distinct block from an image and passes it to a function you specify. blkproc assembles the returned blocks to create an output image.
For example, the command below processes the matrix I in 4-by-6 blocks with the function myfun.
You can specify the function as an inline function. For example,
The example below uses blkproc to set every pixel in each 8-by-8 block of an image matrix to the average of the elements in that block.
I = imread('tire.tif'); f = inline('uint8(round(mean2(x)*ones(size(x))))'); I2 = blkproc(I,[8 8],f); imshow(I) figure, imshow(I2);
Notice that inline computes the mean of the block and then multiplies the result by a matrix of ones, so that the output block is the same size as the input block. As a result, the output image is the same size as the input image. blkproc does not require that the images be the same size; however, if this is the result you want, you must make sure that the function you specify returns blocks of the appropriate size.
Note
blkproc is an example of a "function function." For more information on how to use this kind of function, see the Function Functions section in the MATLAB documentation.
|
 | Linear and Nonlinear Filtering | Overlap |  |