| Financial Time Series Toolbox |   |
Syntax
[transdat, lambda] = boxcox(data) [transfts, lambdas] = boxcox(tsobj) transdat = boxcox(lambda, data) transfts = boxcox(lambda, tsobj)
Arguments
|
Data vector. Must be positive. |
tsobj |
Financial time series object |
Description
boxcox transforms nonnormally distributed data to a set of data that has approximately normal distribution. The Box-Cox transformation is a family of power transformations defined by
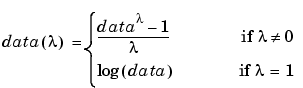
The logarithm is the natural logarithm (log base e). The algorithm calls for finding the 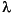 value that maximizes the Log-Likelihood Function (LLF). The search is conducted using
value that maximizes the Log-Likelihood Function (LLF). The search is conducted using fminsearch.
[transdat, lambda] = boxcox(data)
transforms the data vector data using the Box-Cox transformation method into transdat. It also calculates the transformation parameter 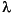 .
.
[transfts, lambda] = boxcox(tsojb)
transforms the financial time series object tsobj using the Box-Cox transformation method into transfts. It also calculates the transformation parameter 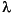 .
.
If the input data is a vector, lambda is a scalar. If the input is a financial time series object, lambda is a structure with fields similar to the components of the object, e.g., if the object contains series names Open and Close, lambda has fields lambda.Open and lambda.Close.
transdat = boxcox(lambda, data) and
transfts = boxcox(lambda, tsobj) transform the data using a certain specified 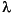 for the Box-Cox transformation. This syntax does not find the optimum
for the Box-Cox transformation. This syntax does not find the optimum 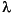 that maximizes the LLF.
that maximizes the LLF.
See Also
 | bollinger | busdays |  |