| Fixed-Point Blockset |   |
Perform the specified bitwise operation on the inputs
Library
Description
The Bitwise Operator block is a masked S-function that performs the specified bitwise operation on its operands.
Unlike the logic operations performed by the Logical Operator block, bitwise operations treat the operands as a vector of bits rather than a single number. You select the bitwise Boolean operation with the Operator parameter list. The supported operations are given below.
Unlike the Simulink Bitwise Logical Operator block, the Bitwise Operator block does not support shift operations. Refer to Shifts to learn how to perform shift operations with the Fixed-Point Blockset.
The size of the output depends on the number of inputs, their vector size, and the selected operator:
When configured as a multi-input XOR gate, this block performs an addition- modulo-two operation as mandated by the IEEE Standard for Logic Elements.
If the Use bit mask check box is not selected, then the block can accept multiple inputs. You select the number of input ports with the Number of input ports parameter. The input data types must be identical.
If the Use bit mask check box is selected, then a single input is associated with the bit mask you specify with the Bit Mask parameter. You specify the bit mask using any valid MATLAB expression. For example, you can specify the bit mask 00100101 as 2^5+2^2+2^0. Alternatively, you can use strings to specify a hexadecimal bit mask such as {'FE73','12AC'}. If the bit mask is larger than the input signal data type, then it is ignored.
The Treat mask as parameter list controls how the mask is treated. The possible values are Real World Value and Stored Integer. In terms of the general encoding scheme described in Scaling, Real World Value treats the mask as V = SQ + B where S is the slope and B is the bias. Stored Integer treats the mask as a stored integer, Q. For more information about this parameter list, refer to the Gateway In block.
Remarks
You can use the bit mask to perform a bit set or a bit clear on the input. To perform a bit set, you configure the Operator parameter list to OR and create a bit mask with a 1 for each corresponding input bit that you want to set to 1. To perform a bit clear, you configure the Operator parameter list to AND and create a bit mask with a 0 for each corresponding input bit that you want to set to 0.
For example, suppose you want to perform a bit set on the fourth bit of an 8-bit input vector. The bit mask would be 00010000, which you can specify as 2^4 in the Bit mask parameter. To perform a bit clear, the bit mask would be 11101111, which you can specify as 2^7+2^6+2^5+2^3+2^2+2^1+2^0 in the Bit mask parameter.
Parameters and Dialog Box
Conversions
The Bit Mask parameter is converted from a double to the input data type offline using round-to-nearest and saturation. Refer to Parameter Conversions for more information about parameter conversions.
Examples
To help you understand the Bitwise Operator block logic operations, consider the fixed-point model shown below.
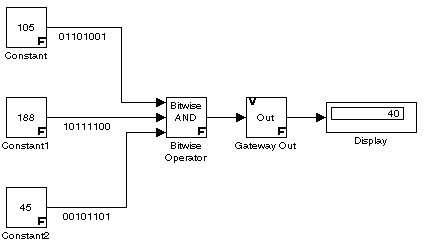
The Constant blocks are configured to output an 8-bit unsigned integer (uint(8)). The results for all logic operations are shown below.
| Operation |
Binary Value |
Decimal Value |
| AND |
00101000 |
40 |
| OR |
11111101 |
253 |
| NAND |
11010111 |
215 |
| NOR |
00000010 |
2 |
| XOR |
11111000 |
248 |
| NOT |
N/A |
N/A |
Characteristics
| Input Port |
Any data type supported by the blockset |
| Output Port |
Same as the input |
| Direct Feedthrough |
No |
| Scalar Expansion |
Of inputs |
 | Bit Set | Compare To Constant |  |