

| Function Reference |   |
Syntax
Description
rlocus
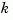 (assuming negative feedback). Root loci are used to study the effects of varying feedback gains on closed-loop pole locations. In turn, these locations provide indirect information on the time and frequency responses.
(assuming negative feedback). Root loci are used to study the effects of varying feedback gains on closed-loop pole locations. In turn, these locations provide indirect information on the time and frequency responses.
rlocus(sys)
calculates and plots the root locus of the open-loop SISO model sys. This function can be applied to any of the following negative feedback loops by setting sys appropriately.
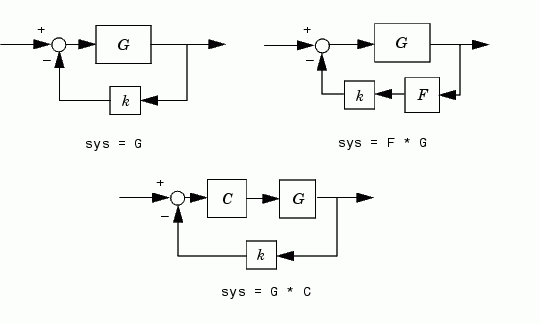
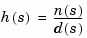
the closed-loop poles are the roots of
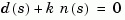
rlocus adaptively selects a set of positive gains 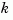 to produce a smooth plot. Alternatively,
to produce a smooth plot. Alternatively,
uses the user-specified vector k of gains to plot the root locus.
rlocus(sys1,sys2,...) draws the root loci of multiple LTI models sys1, sys2,... on a single plot. You can specify a color, line style, and marker for each model, as in
When invoked with output arguments,
return the vector k of selected gains and the complex root locations r for these gains. The matrix r has length(k) columns and its jth column lists the closed-loop roots for the gain k(j).
Example
Find and plot the root-locus of the following system.
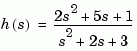
You can use the right-click menu for rlocus to add grid lines, zoom in or out, and invoke the Property Editor to customize the plot. Also, click anywhere on the curve to activate a data marker that displays the gain value, pole, damping, overshoot, and frequency at the selected point.
See Also
pole
pzmap
 | reshape | rss |  |