

| Function Reference |   |
Compute the Padé approximation of models with time delays
Syntax
Description
pade
approximates time delays by rational LTI models. Such approximations are useful to model time delay effects such as transport and computation delays within the context of continuous-time systems. The Laplace transform of an time delay of 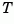 seconds is
seconds is 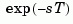 . This exponential transfer function is approximated by a rational transfer function using the Padé approximation formulas [1].
. This exponential transfer function is approximated by a rational transfer function using the Padé approximation formulas [1].
[num,den] = pade(T,N)
returns the Nth-order (diagonal) Padé approximation of the continuous-time I/O delay 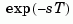 in transfer function form. The row vectors
in transfer function form. The row vectors num and den contain the numerator and denominator coefficients in descending powers of 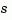 . Both are
. Both are Nth-order polynomials.
When invoked without output arguments,
plots the step and phase responses of the Nth-order Padé approximation and compares them with the exact responses of the model with I/O delay T. Note that the Padé approximation has unit gain at all frequencies.
sysx = pade(sys,N)
produces a delay-free approximation sysx of the continuous delay system sys. All delays are replaced by their Nth-order Padé approximation. See Time Delays for details on LTI models with delays.
sysx = pade(sys,NI,NO,Nio) specifies independent approximation orders for each input, output, and I/O delay. These approximation orders are given by the arrays of integers NI, NO, and Nio, such that:
NI(j) is the approximation order for the j-th input channel.
NO(i) is the approximation order for the i-th output channel.
Nio(i,j) is the approximation order for the I/O delay from input j to output i.
You can use scalar values to specify uniform approximation orders, and [] if there are no input, output, or I/O delays.
Example
Compute a third-order Padé approximation of a 0.1 second I/O delay and compare the time and frequency responses of the true delay and its approximation. To do this, type
Limitations
High-order Padé approximations produce transfer functions with clustered poles. Because such pole configurations tend to be very sensitive to perturbations, Padé approximations with order N>10 should be avoided.
See Also
c2d Discretization of continuous system
delay2z Changes transfer functions of discrete-time LTI models
with delays to rational functions or absorbs FRD delays
into the frequency response phase information
References
[1] Golub, G. H. and C. F. Van Loan, Matrix Computations, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 1989, pp. 557-558.
 | ord2 | parallel |  |