

| Function Reference |   |
Compute gain and phase margins and associated crossover frequencies
Syntax
Description
margin
calculates the minimum gain margin, phase margin, and associated crossover frequencies of SISO open-loop models. The gain and phase margins indicate the relative stability of the control system when the loop is closed. When invoked without left-hand arguments, margin produces a Bode plot and displays the margins on this plot.
The gain margin is the amount of gain increase required to make the loop gain unity at the frequency where the phase angle is -180°. In other words, the gain margin is 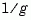 if
if 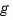 is the gain at the -180° phase frequency. Similarly, the phase margin is the difference between the phase of the response and -180° when the loop gain is 1.0. The frequency at which the magnitude is 1.0 is called the unity-gain frequency or crossover frequency. It is generally found that gain margins of three or more combined with phase margins between 30 and 60 degrees result in reasonable trade-offs between bandwidth and stability.
is the gain at the -180° phase frequency. Similarly, the phase margin is the difference between the phase of the response and -180° when the loop gain is 1.0. The frequency at which the magnitude is 1.0 is called the unity-gain frequency or crossover frequency. It is generally found that gain margins of three or more combined with phase margins between 30 and 60 degrees result in reasonable trade-offs between bandwidth and stability.
[Gm,Pm,Wcg,Wcp] = margin(sys)
computes the gain margin Gm, the phase margin Pm, and the corresponding crossover frequencies Wcg and Wcp, given the SISO open-loop model sys. This function handles both continuous- and discrete-time cases. When faced with several crossover frequencies, margin returns the smallest gain and phase margins.
[Gm,Pm,Wcg,Wcp] = margin(mag,phase,w)
derives the gain and phase margins from the Bode frequency response data (magnitude, phase, and frequency vector). Interpolation is performed between the frequency points to estimate the margin values. This approach is generally less accurate.
When invoked without left-hand argument,
plots the open-loop Bode response with the gain and phase margins marked by vertical lines.
Example
You can compute the gain and phase margins of the open-loop discrete-time transfer function. Type
Transfer function: 0.04798 z + 0.0464 --------------------- z^2 - 1.81 z + 0.9048 Sampling time: 0.1
You can also display these margins graphically.
Algorithm
The phase margin is computed using 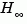 theory, and the gain margin by solving
theory, and the gain margin by solving 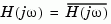 for the frequency
for the frequency 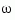 .
.
See Also
bode
ltiview
 | lyap | minreal |  |