| Creating and Manipulating Models |   |
Specifying Delays on the Inputs or Outputs
While ideal for frequency-domain models with I/O delays, the ioDelay property is inadequate to capture delayed inputs or outputs in state-space models. For example, the two models
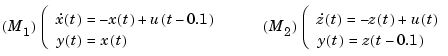
share the same transfer function
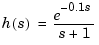
As a result, they cannot be distinguished using the ioDelay property (the I/O delay value is 0.1 seconds in both cases). Yet, these two models have different state trajectories since 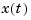 and
and 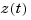 are related by
are related by
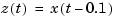
Note that the 0.1 second delay is on the input in the first model, and on the output in the second model.
InputDelay and OutputDelay Properties
When the state trajectory is of interest, you should use the InputDelay and OutputDelay properties to distinguish between delays on the inputs and delays on the outputs in state-space models. For example, you can accurately specify the two models above by
In the MIMO case, you can specify a different delay for each input (or output) channel by assigning a vector value to InputDelay (or OutputDelay). For example,
creates the two-input, two-output model
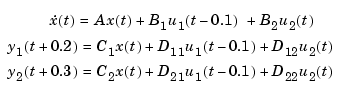
You can also use the InputDelay and OutputDelay properties to conveniently specify input or output delays in TF, ZPK, or FRD models. For example, you can create the transfer function
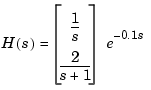
The resulting model is displayed as
By comparison, to produce an equivalent transfer function using the ioDelay property, you would need to type
Notice that the 0.1 second delay is repeated twice in the I/O delay matrix. More generally, for a TF, ZPK, or FRD model with input delays 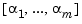 and output delays
and output delays 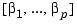 , the equivalent I/O delay matrix is
, the equivalent I/O delay matrix is
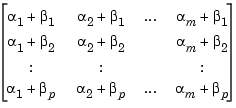
 | Specifying Input/Output Delays | Specifying Delays in Discrete-Time Models |  |