| Creating and Manipulating Models |   |
Specifying Input/Output Delays
Using the ioDelay property, you can specify frequency-domain models with independent delays in each entry of the transfer function. In continuous time, such models have a transfer function of the form
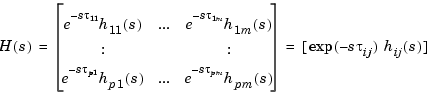
where the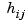 's are rational functions of
's are rational functions of 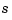 , and
, and 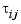 is the time delay between input
is the time delay between input 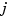 and output
and output 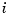 . See Specifying Delays in Discrete-Time Models for details on the discrete-time counterpart. We collectively refer to the scalars
. See Specifying Delays in Discrete-Time Models for details on the discrete-time counterpart. We collectively refer to the scalars 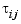 as the I/O delays.
as the I/O delays.
num, den (respectively, z, p, k) specify the rational part 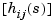 of the transfer function
of the transfer function 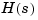
Tau is the matrix of time delays for each I/O pair. That is, Tau(i,j) specifies the I/O delay 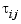 in seconds. Note that
in seconds. Note that Tau and 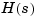 should have the same row and column dimensions.
should have the same row and column dimensions.
You can also use the ioDelay property in conjunction with state-space models, as in
This creates the LTI model with the following transfer function.
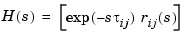
| Note State-space models with I/O delays have only a frequency-domain interpretation. They cannot, in general, be described by state-space equations with delayed inputs and outputs. |
Distillation Column Example
This example is adapted from [2] and illustrates the use of I/O delays in process modeling. The process of interest is the distillation column depicted by the figure below. This column is used to separate a mix of methanol and water (the feed) into bottom products (mostly water) and a methanol-saturated distillate.
Figure 1-3: Distillation Column
Schematically, the distillation process functions as follows:
The regulated output variables are:
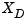 of methanol in the distillate
of methanol in the distillate
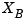 of methanol in the bottom products.
of methanol in the bottom products.
The goal is to maximize 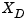 by adjusting the reflux flow rate
by adjusting the reflux flow rate 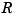 and the steam flow rate
and the steam flow rate 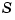 in the reboiler.
in the reboiler.
To obtain a linearized model around the steady-state operating conditions, the transient responses to pulses in steam and reflux flow are fitted by first-order plus delay models. The resulting transfer function model is
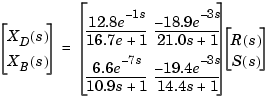
Note the different time delays for each input/output pair.
You can specify this MIMO transfer function by typing
H = tf({12.8 -18.9;6.6 -19.4},... {[16.7 1] [21 1];[10.9 1] [14.4 1]},... 'iodelay',[1 3;7 3],... 'inputname',{'R' , 'S'},... 'outputname',{'Xd' , 'Xb'})
The resulting TF model is displayed as
Transfer function from input "R" to output... 12.8 Xd: exp(-1*s) * ---------- 16.7 s + 1 6.6 Xb: exp(-7*s) * ---------- 10.9 s + 1 Transfer function from input "S" to output... -18.9 Xd: exp(-3*s) * -------- 21 s + 1 -19.4 Xb: exp(-3*s) * ---------- 14.4 s + 1
 | Supported Functionality | Specifying Delays on the Inputs or Outputs |  |