| MATLAB Compiler |   |
The MATLAB Compiler Family
This figure illustrates the various ways you can use the MATLAB Compiler. The shaded blocks represent user-written code; the unshaded blocks represent Compiler-generated code; the remaining blocks (drop shadow) represent MathWorks or other vendor tools.
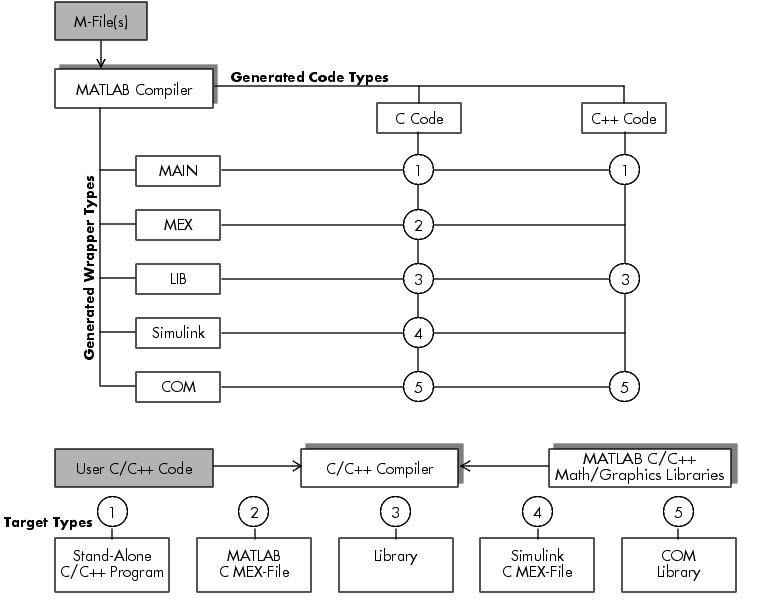
Figure 1-3: MATLAB Compiler Uses
The Compiler takes your M-file(s) and can generate C or C++ code. It can also generate a wrapper file depending on your specified target. This table shows the wrapper files the Compiler can generate, their associated targets, and the corresponding -W option (wrapper).
Each numbered node in Figure 1-3, MATLAB Compiler Uses, indicates a combination of C/C++ code and a wrapper that generates a specific target type. The file(s) formed by combining the C/C++ code (denoted by "User C/C++ Code") and the wrapper are then passed to the C/C++ compiler, which combines them with any user-defined C/C++ programs, and eventually links them against the appropriate libraries. The end result of this sequence is the target as described in the table above.
 | Creating Stand-Alone Applications | Why Compile M-Files? |  |