| Function Reference |   |
Specify discrete transfer functions in DSP format
Syntax
sys = filt(num,den) sys = filt(num,den,Ts) sys = filt(M) sys = filt(num,den,'Property1',Value1,...,'PropertyN',ValueN) sys = filt(num,den,Ts,'Property1',Value1,...,'PropertyN',ValueN)
Description
In digital signal processing (DSP), it is customary to write transfer functions as rational expressions in 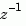 and to order the numerator and denominator terms in ascending powers of
and to order the numerator and denominator terms in ascending powers of 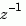 , for example,
, for example,
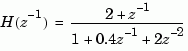
The function filt is provided to facilitate the specification of transfer functions in DSP format.
sys = filt(num,den)
creates a discrete-time transfer function sys with numerator(s) num and denominator(s) den. The sample time is left unspecified (sys.Ts = -1) and the output sys is a TF object.
sys = filt(num,den,Ts)
further specifies the sample time Ts (in seconds).
sys = filt(M)
M.
Any of the previous syntaxes can be followed by property name/property value pairs of the form
Each pair specifies a particular LTI property of the model, for example, the input names or the transfer function variable. See LTI Properties and the set entry for additional information on LTI properties and admissible property values.
Arguments
For SISO transfer functions, num and den are row vectors containing the numerator and denominator coefficients ordered in ascending powers of 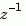 . For example,
. For example, den = [1 0.4 2] represents the polynomial 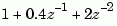 .
.
MIMO transfer functions are regarded as arrays of SISO transfer functions (one per I/O channel), each of which is characterized by its numerator and denominator. The input arguments num and den are then cell arrays of row vectors such that:
num and den have as many rows as outputs and as many columns as inputs.
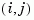 entries
entries num{i,j} and den{i,j} specify the numerator and denominator of the transfer function from input j to output i.
If all SISO entries have the same denominator, you can also set den to the row vector representation of this common denominator. See also MIMO Transfer Function Models for alternative ways to specify MIMO transfer functions.
Remark
filt behaves as tf with the Variable property set to 'z^-1' or 'q'. See tf entry below for details.
Example
creates the two-input digital filter
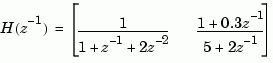
with unspecified sample time and input names 'channel1' and 'channel2'.
See Also
tf
zpk
ss
 | feedback | frd |  |