| Optimization Toolbox |   |
Nonlinear Inequality Constrained Example
If inequality constraints are added to Eq. 2-1, the resulting problem can be solved by the fmincon function. For example, find x that solves
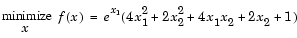
|
(2-2) |
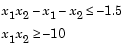
Because neither of the constraints is linear, you cannot pass the constraints to fmincon at the command line. Instead you can create a second M-file, confun.m, that returns the value at both constraints at the current x in a vector c. The constrained optimizer, fmincon, is then invoked. Because fmincon expects the constraints to be written in the form 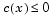 , you must rewrite your constraints in the form
, you must rewrite your constraints in the form
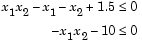
|
(2-3) |
Step 1: Write an M-file confun.m for the constraints.
function [c, ceq] = confun(x) % Nonlinear inequality constraints c = [1.5 + x(1)*x(2) - x(1) - x(2); -x(1)*x(2) - 10]; % Nonlinear equality constraints ceq = [];
Step 2: Invoke constrained optimization routine.
x0 = [-1,1]; % Make a starting guess at the solution options = optimset('LargeScale','off'); [x, fval] = ... fmincon(@objfun,x0,[],[],[],[],[],[],@confun,options)
After 38 function calls, the solution x produced with function value fval is
We can evaluate the constraints at the solution
Note that both constraint values are less than or equal to zero; that is, x satisfies 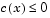 .
.
 | Unconstrained Minimization Example | Constrained Example with Bounds |  |