| Wavelet Toolbox |   |
Syntax
Description
[PHI,PSI,T] = meyer(LB,UB,N) returns Meyer scaling and wavelet functions evaluated on an N point regular grid in the interval [LB,UB].
Output arguments are the scaling function PHI and the wavelet function PSI computed on the grid T. These functions have [-8 8] as effective support.
If only one function is required, a fourth argument is allowed:
When the fourth argument is used, but not equal to 'phi' or 'psi', outputs are the same as in the main option.
The Meyer wavelet and scaling function are defined in the frequency domain:
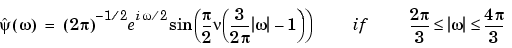
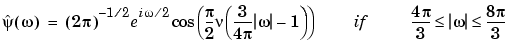
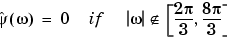
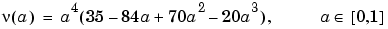
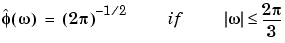
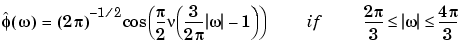
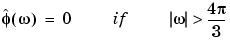
By changing the auxiliary function (see meyeraux for more information), you get a family of different wavelets. For the required properties of the auxiliary function 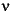 , see "References" in Chapter 6, "Advanced Concepts", of the User's Guide.
, see "References" in Chapter 6, "Advanced Concepts", of the User's Guide.
Examples
% Set effective support and grid parameters. lb = -8; ub = 8; n = 1024; % Compute and plot Meyer wavelet and scaling functions. [phi,psi,x] = meyer(lb,ub,n); subplot(211), plot(x,psi) title('Meyer wavelet') subplot(212), plot(x,phi) title('Meyer scaling function')
Algorithm
Starting from an explicit form of the Fourier transform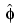 of
of 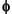 ,
, meyer computes the values of 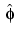 on a regular grid, and then the values of
on a regular grid, and then the values of 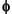 are computed using
are computed using instdfft, the inverse nonstandard discrete FFT.
The procedure for 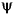 is along the same lines.
is along the same lines.
See Also
meyeraux, wavefun, waveinfo
References
Daubechies I. (1992), Ten lectures on wavelets, CBMS-NSF conference series in applied mathematics. SIAM Ed. pp. 117-119, 137, 152.
 | mexihat | meyeraux |  |