| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Capability Studies
Before going into full-scale production, many manufacturers run a pilot study to determine whether their process can actually build parts to the specifications demanded by the engineering drawing.
Using the data from these capability studies with a statistical model allows us to get a preliminary estimate of the percentage of parts that will fall outside the specifications.
The result above shows that the probability (p = 1.3940e-09) of observing an unacceptable runout is extremely low. Cp and Cpk are two popular capability indices.
Cp is the ratio of the range of the specifications to six times the estimate of the process standard deviation.
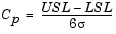
For a process that has its average value on target, a Cp of 1 translates to a little more than one defect per thousand. Recently many industries have set a quality goal of one part per million. This would correspond to a Cp = 1.6. The higher the value of Cp, the more capable the process.
Cpk is the ratio of difference between the process mean and the closer specification limit to three times the estimate of the process standard deviation.
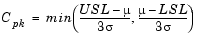
where the process mean is µ. For processes that do not maintain their average on target, Cpk, is a more descriptive index of process capability.
 | EWMA Charts | Design of Experiments |  |