| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Syntax
Description
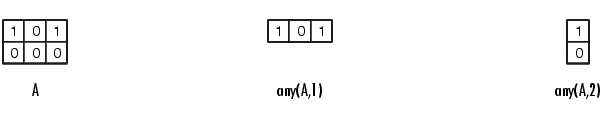
B = any(A)
tests whether any of the elements along various dimensions of an array are nonzero or logical true (1).
If A is a vector, any(A) returns logical true (1) if any of the elements of A are nonzero, and returns logical false (0) if all the elements are zero.
If A is a matrix, any(A) treats the columns of A as vectors, returning a row vector of 1s and 0s.
If A is a multidimensional array, any(A) treats the values along the first non-singleton dimension as vectors, returning a logical condition for each vector.
B = any(A, tests along the dimension of dim)
A specified by scalar dim.
Examples
then B = (A < 0.5) returns logical true (1) only where A is less than one half:
The any function reduces such a vector of logical conditions to a single condition. In this case, any(B) yields 1.
This makes any particularly useful in if statements,
where code is executed depending on a single condition, not a vector of possibly conflicting conditions.
Applying the any function twice to a matrix, as in any(any(A)), always reduces it to a scalar condition.
See Also
all, logical operators, relational operators, colon
Other functions that collapse an array's dimensions include:
max, mean, median, min, prod, std, sum, trapz
 | ans | area |  |