

| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Syntax
Description
y = var(X)
x. For matrices, var(X) is a row vector containing the variance of each column of X.
y = var(x)
var(x) the minimum variance unbiased estimator MVUE of 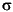 2(the second parameter).
2(the second parameter).
y = var(x,1)
y = var(X,w)
w. The number of elements in w must equal the number of rows in the matrix X. For vector x, w and x must match in length.
var supports both common definitions of variance. Let SS be the sum of
the squared deviations of the elements of a vector x from their mean. Then, var(x) = SS/(n-1) is the MVUE, and var(x,1) = SS/n is the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) of 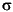 2.
2.
Examples
 | unifstat | weibcdf |  |