

| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Mean absolute deviation (MAD) of a sample of data
Syntax
Description
y = mad(X)
computes the average of the absolute differences between a set of data and the sample mean of that data. For vectors, mad(x) returns the mean absolute deviation of the elements of x. For matrices, mad(X) returns the MAD of each column of X.
The MAD is less efficient than the standard deviation as an estimate of the spread when the data is all from the normal distribution.
Multiply the MAD by 1.3 to estimate 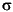 (the second parameter of the normal distribution).
(the second parameter of the normal distribution).
Examples
This example shows a Monte Carlo simulation of the relative efficiency of the MAD to the sample standard deviation for normal data.
x = normrnd(0,1,100,100); s = std(x); s_MAD = 1.3 * mad(x); efficiency = (norm(s - 1)./norm(s_MAD - 1)).^2 efficiency = 0.5972
 | lsline | mahal |  |