

| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Gamma probability density function (pdf)
Syntax
Description
gampdf(X,A,B)
computes the gamma pdf at each of the values in X using the corresponding parameters in A and B. Vector or matrix inputs for X, A, and B must all be the same size. A scalar input is expanded to a constant matrix with the same dimensions as the other inputs. The parameters in A and B must all be positive, and the values in X must lie on the interval [0 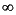 ).
).
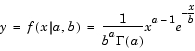
The gamma probability density function is useful in reliability models of lifetimes. The gamma distribution is more flexible than the exponential distribution in that the probability of a product surviving an additional period may depend on its current age. The exponential and 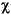 2 functions are special cases of the gamma function.
2 functions are special cases of the gamma function.
Examples
The exponential distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution.
mu = 1:5; y = gampdf(1,1,mu) y = 0.3679 0.3033 0.2388 0.1947 0.1637 y1 = exppdf(1,mu) y1 = 0.3679 0.3033 0.2388 0.1947 0.1637
See Also
gamcdf, gamfit, gaminv, gamlike, gamrnd, gamstat, pdf
 | gamlike | gamrnd |  |