| Stateflow |   |
Tips and Tricks for Using Fixed-Point Data in Stateflow
Once you specify fixed-point data (see Specifying Fixed-Point Data in Stateflow), you can use it just as you would any data in Stateflow. However, because of the limitations of fixed-point numbers, it is a good idea to follow these guidelines when using them:
Stateflow uses this integer size in generated code to select result types for your fixed-point operations. See Setting the Integer Word Size for a Target.
This suffix casts a literal numeric constant in the type of its context. For example, if x is fixed-point data, the expression y = x/3.2C first converts the numerical constant 3.2 to the fixed-point type of x and then performs the division with a fixed-point result. See Fixed-Point Context-Sensitive Constants for more information.
For example, you might want to increase 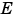 from -2 to -1. This decreases the available precision in your fixed-point data.
from -2 to -1. This decreases the available precision in your fixed-point data.
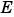 .
.
For example, you might want to decrease 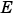 from -2 to -3. This decreases the available range in your fixed-point data.
from -2 to -3. This decreases the available range in your fixed-point data.
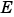 , you might also want to increase the number of bits in the base data type for
, you might also want to increase the number of bits in the base data type for 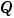 to prevent overflow.
to prevent overflow.
:= assignment operator in place of the = operator for assigning the results of multiplication and division operations.
:= operator to increase the range and precision of the result of fixed-point multiplication and division operations at the possible expense of computational efficiency. See Assignment Operator :=.
 | Specifying Fixed-Point Data in Stateflow | Offline and Online Conversions of Fixed-Point Data |  |