| Stateflow |   |
How Stateflow Implements Fixed-Point Data
The preceding example in Fixed-Point Arithmetic does not answer the question of how the values for the slope, 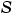 , the quantized integer,
, the quantized integer, 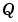 , and the bias,
, and the bias, 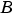 , are implemented in Stateflow as integers. These values are implemented through the following:
, are implemented in Stateflow as integers. These values are implemented through the following:
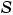 ,
, 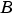 , and the base integer type for
, and the base integer type for 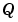 . The available base types for
. The available base types for 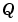 are the unsigned integer types
are the unsigned integer types uint8, uint16, and uint32, and the signed integer types int8, int16, and int32. For specific instructions on how to enter fixed-point data, see Specifying Fixed-Point Data in Stateflow.
Notice that if a fixed-point number has a slope 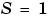 and a bias
and a bias 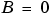 , it is equivalent to its quantized integer
, it is equivalent to its quantized integer 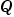 , and behaves exactly as its base integer type.
, and behaves exactly as its base integer type.
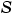 and
and 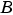 are constant and appear only as literal numbers or expressions in generated code.
are constant and appear only as literal numbers or expressions in generated code.
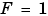 avoids the computationally expensive multiply instructions for values of
avoids the computationally expensive multiply instructions for values of 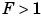 . This is referred to as radix point-only scaling, which is implemented with bit shifts only, and is highly recommended.
. This is referred to as radix point-only scaling, which is implemented with bit shifts only, and is highly recommended.
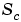 and
and 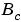 that conveniently cancel out difficult terms in the solutions. See Addition (+) and Subtraction (-) and Multiplication (*) and Division (/).
that conveniently cancel out difficult terms in the solutions. See Addition (+) and Subtraction (-) and Multiplication (*) and Division (/).
Stateflow provides a special assignment operator (:=) and context-sensitive constants to help you maintain as much precision as possible in your fixed-point operations. See Assignment (=, :=) and Cast Operations and Fixed-Point Context-Sensitive Constants.
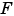 , that cannot be expressed as a pure integer or a power of 2, are converted into fixed-point numbers.
, that cannot be expressed as a pure integer or a power of 2, are converted into fixed-point numbers.
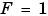 and
and 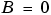 is recommended.
is recommended.
 | Fixed-Point Arithmetic | Specifying Fixed-Point Data in Stateflow |  |