

| Simulink Reference |   |
Delay the input by a variable amount of time
Library
Description
The Variable Transport Delay block can be used to simulate a variable time delay. The block might be used to model a system with a pipe where the speed of a motor pumping fluid in the pipe is variable.
The block accepts two inputs: the first input is the signal that passes through the block; the second input is the time delay, as shown in this icon.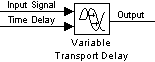
The Maximum delay parameter defines the largest value the time delay input can have. The block clips values of the delay that exceed this value. The Maximum delay must be greater than or equal to zero. If the time delay becomes negative, the block clips it to zero and issues a warning message.
During the simulation, the block stores time and input value pairs in an internal buffer. At the start of the simulation, the block outputs the Initial input parameter until the simulation time exceeds the time delay input. Then, at each simulation step the block outputs the signal at the time that corresponds to the current simulation time minus the delay time.
When output is required at a time that does not correspond to the times of the stored input values, the block interpolates linearly between points. If the time delay is smaller than the step size, the block extrapolates an output point. This can result in less accurate results. The block cannot use the current input to calculate its output value because the block does not have direct feedthrough at this port. To illustrate this point, consider a fixed-step simulation with a step size of 1 and the current time at t = 5. If the delay is 0.5, the block needs to generate a point at t = 4.5. Because the most recent stored time value is at t = 4, the block performs forward extrapolation.
The Variable Transport Delay block does not interpolate discrete signals. Instead, it returns the discrete value at t - tdelay.
Data Type Support
A Variable Transport Delay block accepts and outputs real signals of type double.
Parameters and Dialog Box
10.0.1024.0, which results in a unity gain with no dynamic states. Setting the order to a positive integer n adds n states to your model, but results in a more accurate linear model of the transport delay.Characteristics
| Direct Feedthrough |
Yes, of the time delay (second) input |
| Sample Time |
Continuous |
| Scalar Expansion |
Of input and all parameters except Buffer size |
| Dimensionalized |
Yes |
| Zero Crossing |
No |
 | Unit Delay | While Iterator |  |