

| Image Processing Toolbox |   |
Perform two-dimensional adaptive noise-removal filtering
Syntax
Description
wiener2 lowpass filters an intensity image that has been degraded by constant power additive noise. wiener2 uses a pixel-wise adaptive Wiener method based on statistics estimated from a local neighborhood of each pixel.
J = wiener2(I,[m n],noise) filters the image I using pixel-wise adaptive Wiener filtering, using neighborhoods of size m-by-n to estimate the local image mean and standard deviation. If you omit the [m n] argument, m and n default to 3. The additive noise (Gaussian white noise) power is assumed to be noise.
[J,noise] = wiener2(I,[m n]) also estimates the additive noise power before doing the filtering. wiener2 returns this estimate in noise.
Class Support
The input image, I, is a two-dimensional image of class uint8, uint16, or double. The output image, J, is of the same size and class as I.
Example
Degrade and then restore an intensity image using adaptive Wiener filtering.
I = imread('saturn.tif'); J = imnoise(I,'gaussian',0,0.005); K = wiener2(J,[5 5]); imshow(J) figure, imshow(K)
Algorithm
wiener2 estimates the local mean and variance around each pixel
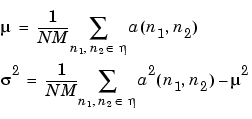
where 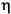 is the N-by-M local neighborhood of each pixel in the image
is the N-by-M local neighborhood of each pixel in the image A. wiener2 then creates a pixel-wise Wiener filter using these estimates
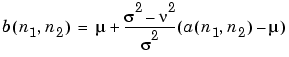
where 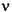 2 is the noise variance. If the noise variance is not given,
2 is the noise variance. If the noise variance is not given, wiener2 uses the average of all the local estimated variances.
See Also
Reference
[1] Lim, Jae S. Two-Dimensional Signal and Image Processing. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1990. pp. 536-540.
 | watershed | ycbcr2rgb |  |