

| System Identification Toolbox |   |
The Basic Dynamic Model
The basic relationship is the linear difference equation. An example of such an equation is the following one.
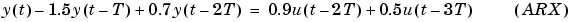
Such a relationship tells us, for example, how to compute the output y(t) if the input is known and the disturbance can be ignored:
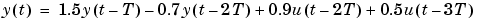
The output at time t is thus computed as a linear combination of past outputs and past inputs. It follows, for example, that the output at time t depends on the input signal at many previous time instants. This is what the word dynamic refers to. The identification problem is then to use measurements of u and y to figure out:
 | The Signals | Variants of Model Descriptions |  |