| Fixed-Point Blockset |   |
Implement a fixed-point finite impulse response (FIR) filter
Library
Description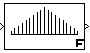
The FIR block is a masked S-function that samples and holds the N most recent inputs, multiplies each input by a specified value (its FIR coefficient), and stacks them in a vector. This block supports both single-input/single-output (SISO) and single-input/multi-output (SIMO) modes.
For the SISO mode, the FIR coefficients parameter is specified as a row vector. For the SIMO mode, the FIR coefficients are specified as a matrix where each row corresponds to a separate output.
The Initial condition parameter provides the initial values for all times preceding the start time in the FIR realization. You specify the time interval between samples with the Sample time parameter.
You can choose whether or not to specify the data type and scaling of the FIR coefficients in the dialog with the Gain data type and scaling parameter. If you select Specify via dialog for this parameter, the Parameter data type and Parameter scaling parameters become visible.
You can specify the scaling for the FIR coefficients with the Parameter scaling parameter. Note that there are two dialog box parameters that control the FIR coefficient scaling: one associated with an edit field, and one associated with a parameter list. If Parameter data type is a generalized fixed-point number such as sfix(16), the Parameter scaling list provides you with these scaling modes:
Use Specified Scaling--This mode uses the [Slope Bias] or radix point-only scaling specified for the editable Parameter scaling parameter (for example, 2^-10).
Best Precision: Element-wise--This mode produces radix points such that the precision is maximized for each element of the FIR coefficients parameter.
Best Precision: Row-wise--This mode produces a common radix point for each element of the FIR coefficients row based on the best precision for the largest value of that row.
Best Precision: Column-wise--This mode produces a common radix point for each element of the FIR coefficients column based on the best precision for the largest value of that column.
Best Precision: Matrix-wise--This mode produces a common radix point for each element of the FIR coefficients matrix based on the best precision for the largest value of the matrix.
If the FIR coefficients are specified as a row vector, then scaling element-wise and column-wise produce the same result, while scaling matrix-wise and row-wise produce the same result.
For a detailed description of all other block parameters, refer to Block Parameters.
Parameters and Dialog Box
Specify via dialog is selected, the Parameter data type and Parameter scaling parameters become visible.Specify via dialog is selected for the Gain data type and scaling parameter.Specify via dialog is selected for the Gain data type and scaling parameter.Specify via dialog is selected for the Gain data type and scaling parameter.Conversions and Operations
The FIR coefficients parameter is converted from doubles to the specified data type offline using round-to-nearest and saturation.The Initial condition parameter is converted from doubles to the input data type offline using round-to-nearest and saturation. Refer to Parameter Conversions for more information about parameter conversions.
The FIR block first multiplies its inputs by the FIR coefficients parameter, converts those results to the output data type using the specified rounding and overflow modes, and then carries out the summation. Refer to Rules for Arithmetic Operations for more information about the rules this block adheres to when performing operations.
Examples
Suppose you want to configure this block for two outputs (SIMO mode) where the first output is given by
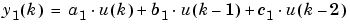
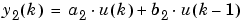
and the initial values of u(k - 1) and u(k - 2) are given by ic1 and ic2, respectively. To configure the FIR block for this situation, you must specify the FIR coefficient parameter as [a1 b1 c1; a2 b2 c2] where c2 = 0, and the Initial condition parameter as [ic1 ic2].
Characteristics
 | Filter Real Zero | Gain |  |