| Fixed-Point Blockset |   |
Example 1: Using errmax with Unrestricted Spacing
The first example shows how to create a lookup table that has the fewest data points for a specified worst case error, with unrestricted spacing. Before trying the example, enter the same parameter values given in the section Setting Function Parameters for the Lookup Table, if you have not already done so in this MATLAB session.
You specify the maximum allowed error by typing
Creating the Lookup Table
To create the lookup table, type
[xdata,ydata,errworst]=fixpt_look1_func_approx(funcstr,... xmin,xmax,xdt,xscale,ydt,yscale,rndmeth,errmax);
Note that the nptsmax and spacing parameters are not specified.
The function returns three variables:
xdata, the vector of breakpoints of the lookup table
ydata, the vector found by applying ideal function, sin(2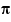 x), to
x), to xdata
errworst, which specifies the maximum possible error in the lookup table
The value of errworst is less than or equal to the value of errmax.
You can find the number of X data points by typing
This means that 16 points are required to approximate sin(2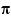 x) to within the tolerance specified by
x) to within the tolerance specified by errmax.
You can display the maximum error by typing errworst. This returns
Plotting the Results
You can plot the output of the function fixpt_look1_func_plot by typing
The resulting plots are shown below.
The upper plot shows the ideal function, sin(2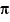 x) and the fixed-point lookup approximation between the breakpoints. In this example, the ideal function and the approximation are so close together that the two graphs appear to coincide. The lower plot displays the errors.
x) and the fixed-point lookup approximation between the breakpoints. In this example, the ideal function and the approximation are so close together that the two graphs appear to coincide. The lower plot displays the errors.
In this example, the Y data points, returned by the function fixpt_look1_func_approx as ydata, are equal to the ideal function applied to the points in xdata. However, you can define a different set of values for ydata after running fixpt_look1_func_plot. This can sometimes reduce the maximum error.
You can also change the values of xmin and xmax in order to evaluate the lookup table on a subset of the original interval.
To find the new maximum error after changing ydata, xmin or xmax, type
 | Setting Function Parameters for the Lookup Table | Example 2: Using nptsmax with Unrestricted Spacing |  |