

| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Sort elements in ascending order
Syntax
Description
B = sort(A)
sorts the elements along different dimensions of an array, and arranges those elements in ascending order.
Real, complex, and string elements are permitted. For elements of A with identical values, the order of these elements is preserved in the sorted list. When A is complex, the elements are sorted by magnitude, i.e., abs(A), and where magnitudes are equal, further sorted by phase angle, i.e., angle(A), on the interval 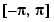 . If
. If A includes any NaN elements, sort places these at the end.
B = sort(A,dim)
sorts the elements along the dimension of A specified by a scalar dim. If dim is a vector, sort works iteratively on the specified dimensions. Thus, sort(A,[1 2]) is equivalent to sort(sort(A,2),1).
[B,IX] = sort(A,...)
also returns an array of indices IX, where size(IX) == size(A). If A is a vector, B = A(IX). If A is an m-by-n matrix, then each column of IX is a permutation vector of the corresponding column of A, such that
If A has repeated elements of equal value, the returned indices preserve the original ordering.
Examples
This example sorts a matrix A in each dimension, and then sorts it a third time, requesting an array of indices for the sorted result.
A = [ 3 7 5 0 4 2 ]; sort(A,1) ans = 0 4 2 3 7 5 sort(A,2) ans = 3 5 7 0 2 4 [B,IX] = sort(A,2) B = 3 5 7 0 2 4 IX = 1 3 2 1 3 2
See Also
max, mean, median, min, sortrows
 | smooth3 | sortrows |  |