| Programming and Data Types |   |
Accessing Data in Structure Arrays
Using structure array indexing, you can access the value of any field or field element in a structure array. Likewise, you can assign a value to any field or field element. For the examples in this section, consider this structure array.
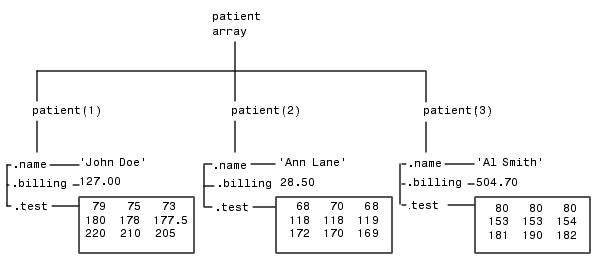
You can access subarrays by appending standard subscripts to a structure array name. For example, the line below results in a 1-by-2 structure array.
The first structure in the mypatients array is the same as the first structure in the patient array.
To access a field of a particular structure, include a period (.) after the structure name followed by the field name.
To access elements within fields, append the appropriate indexing mechanism to the field name. That is, if the field contains an array, use array subscripting; if the field contains a cell array, use cell array subscripting, and so on.
Use the same notations to assign values to structure fields, for example,
You can extract field values for multiple structures at a time. For example, the line below creates a 1-by-3 vector containing all of the billing fields.
Similarly, you can create a cell array containing the test data for the first two structures.
Accessing Data Using Dynamic Field Names
All of the structures discussed up to this point have elements that can only be referenced using fixed field names. Another means of accessing structures is to use dynamic field names. These names express the field as a variable expression that MATLAB evaluates at run-time. The dot-parentheses syntax shown here makes expression a dynamic field name.
Index into this field using the standard MATLAB indexing syntax. For example, to evaluate expression into a field name and obtain the values of that field at columns 1 through 25 of row 7, use
Example. The function avgscore computes an average test score, retrieving information from the testscores structure using dynamic field names.
function avg = avgscore(testscores, student, first, last) for k = first:last scores(k) = testscores.(student).week(k); end avg = sum(scores)/(last - first + 1);
You can run this function using different values for the dynamic field, student.
avgscore(testscores, 'Ann_Lane', 1, 20) ans = 83.5000 avgscore(testscores, 'William_King', 1, 20) ans = 92.1000
 | Building Structure Arrays | Finding the size of Structure Arrays |  |