| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Syntax
quiver(U,V,U,V) quiver(X,Y) quiver(...,scale) quiver(...,LineSpec) quiver(...,LineSpec,'filled') h = quiver(...)
Description
A quiver plot displays velocity vectors as arrows with components (U,V) at the points (X,Y).
For example, the first vector is defined by componets U(1),V(1) and is displayed at the point X(1),Y(1).
quiver(X,Y,U,V)
plots vectors as arrows at the coordinates specifide in each corresponding pair of elements in X and Y. The matirces X, Y, U, and V must all be the same size and contain corresponding position and velocity components.
Expanding X and Y Coordinates
MATLAB expandes X and Y, if they are not matrices. This expansion is equivalent to calling meshgrid to generate matrices from vectors:
[X,Y] = meshgrid(X,Y)
quiver(X,Y,U,V)
In this case, the following must be true:
length(X) = n and length(Y) = m, where [m,n] = size(U) = size(V)
The vector X corresponds to the columns of U and V, and vector Y corresponds to the rows of U and V.
quiver(U,V)
draws vectors specified by U and V at equally spaced points in the x-y plane.
quiver(...,scale)
automatically scales the arrows to fit within the grid and then stretches them by the factor scale. scale = 2 doubles their relative length and scale = 0.5 halves the length. Use scale = 0 to plot the velocity vectors without the automatic scaling.
quiver(..., specifies line style, marker symbol, and color using any valid LineSpec)
LineSpec. quiver draws the markers at the origin of the vectors.
quiver(..., fills markers specified by LineSpec,'filled')
LineSpec.
h = quiver(...)
returns a vector of line handles.
Examples
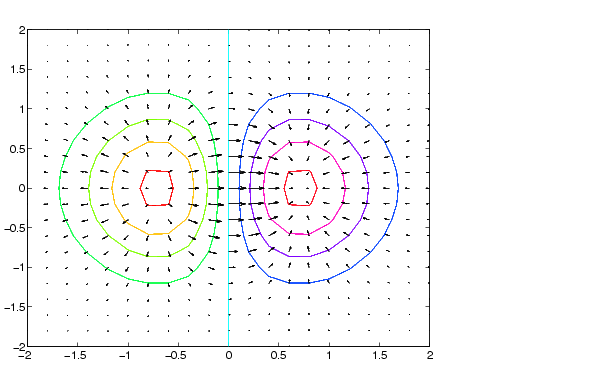
Plot the gradient field of the function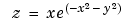 .
.
[X,Y]=meshgrid(-2:.2:2);Z=X.*exp(-X.^2 - Y.^2);[DX,DY] =gradient(Z,.2,.2);contour(X,Y,Z)holdon quiver(X,Y,DX,DY) colormap hsvgridoff hold off
See Also
contour, LineSpec, plot, quiver3
Direction and Velocity Plots for related functions
Two-Dimensional Quiver Plots for more examples
 | quit | quiver3 |  |