| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
One-dimensional data interpolation (table lookup)
Syntax
yi = interp1(x,Y,xi) yi = interp1(Y,xi) yi = interp1(x,Y,xi,method) yi = interp1(x,Y,xi,method,'extrap') yi = interp1(x,Y,xi,method,extrapval)
Description
yi = interp1(x,Y,xi)
yi containing elements corresponding to the elements of xi and determined by interpolation within vectors x and Y. The vector x specifies the points at which the data Y is given. If Y is a matrix, then the interpolation is performed for each column of Y and yi is length(xi)-by-size(Y,2).
yi = interp1(Y,xi)
assumes that x = 1:N, where N is the length of Y for vector Y, or size(Y,1) for matrix Y.
yi = interp1(x,Y,xi,method)
For the 'nearest', 'linear', and 'v5cubic' methods, interp1(x,Y,xi,method) returns NaN for any element of xi that is outside the interval spanned by x. For all other methods, interp1 performs extrapolation for out of range values.
yi = interp1(x,Y,xi,method,'extrap')
uses the specified method to perform extrapolation for out of range values.
yi = interp1(x,Y,xi,method,extrapval)
returns the scalar extrapval for out of range values. NaN and 0 are often used for extrapval.
The interp1 command interpolates between data points. It finds values at intermediate points, of a one-dimensional function 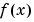 that underlies the data. This function is shown below, along with the relationship between vectors
that underlies the data. This function is shown below, along with the relationship between vectors x, Y, xi, and yi.
Interpolation is the same operation as table lookup. Described in table lookup terms, the table is [x,Y] and interp1 looks up the elements of xi in x, and, based upon their locations, returns values yi interpolated within the elements of Y.
Examples
Example 1. Generate a coarse sine curve and interpolate over a finer abscissa.
Example 2. Here are two vectors representing the census years from 1900 to 1990 and the corresponding United States population in millions of people.
t = 1900:10:1990; p = [75.995 91.972 105.711 123.203 131.669... 150.697 179.323 203.212 226.505 249.633];
The expression interp1(t,p,1975) interpolates within the census data to estimate the population in 1975. The result is
Now interpolate within the data at every year from 1900 to 2000, and plot the result.
Sometimes it is more convenient to think of interpolation in table lookup terms, where the data are stored in a single table. If a portion of the census data is stored in a single 5-by-2 table,
then the population in 1975, obtained by table lookup within the matrix tab, is
Algorithm
The interp1 command is a MATLAB M-file. The 'nearest' and 'linear' methods have straightforward implementations.
For the 'spline' method, interp1 calls a function spline that uses the functions ppval, mkpp, and unmkpp. These routines form a small suite of functions for working with piecewise polynomials. spline uses them to perform the cubic spline interpolation. For access to more advanced features, see the spline reference page, the M-file help for these functions, and the Spline Toolbox.
For the 'pchip' and 'cubic' methods, interp1 calls a function pchip that performs piecewise cubic interpolation within the vectors x and y. This method preserves monotonicity and the shape of the data. See the pchip reference page for more information.
See Also
interpft, interp2, interp3, interpn, pchip, spline
References
[1] de Boor, C., A Practical Guide to Splines, Springer-Verlag, 1978.
 | int8, int16, int32, int64 | interp2 |  |