| Statistics Toolbox |   |
Negative binomial cumulative distribution function (cdf)
Syntax
Description
Y computes the negative binomial cdf at each of the values in = nbincdf(X,R,P)
X using the corresponding parameters in R and P. Vector or matrix inputs for X, R, and P must have the same size, which is also the size of Y. A scalar input for X, R, or P is expanded to a constant matrix with the same dimensions as the other inputs.
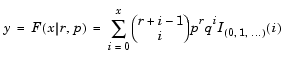
The simplest motivation for the negative binomial is the case of successive random trials, each having a constant probability P of success. The number of extra trials you must perform in order to observe a given number R of successes has a negative binomial distribution. However, consistent with a more general interpretation of the negative binomial, nbincdf allows R to be any positive value, including nonintegers. When R is noninteger, the binomial coefficient in the definition of the cdf is replaced by the equivalent expression
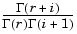
Example
See Also
cdf, nbinfit, nbininv, nbinpdf, nbinrnd, nbinstat
 | nansum | nbinfit |  |