| Creating and Manipulating Models |   |
Building LTI Arrays Using tf, zpk, ss, and frd
You can also build LTI arrays using the tf, zpk, ss, and frd constructors. You do this by using multidimensional arrays in the input arguments for these functions.
Specifying Arrays of TF models tf
sys (see "size and ndims" on page 4-9).
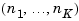 position of the array.
position of the array.
See "MIMO Transfer Function Models" on page 2-10 for related information on the specification of single TF models.
Specifying Arrays of ZPK Models Using zpk
zeros, poles, and gains, determine those of the LTI array, sys.
Specifying Arrays of SS Models Using ss
To specify arrays of SS models, use
where a, b, c, and d are real-valued multidimensional arrays of appropriate dimensions. All models in the resulting array of SS models have the same number of states, outputs, and inputs.
Note
You cannot use the ss constructor to build an array of state-space
models with different numbers of states. Use stack to build such LTI arrays.
|
The Size of LTI Array Data for SS Models
The size of the model data for arrays of state-space models is summarized in the following table.
| Data |
Size (Data) |
a |
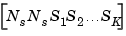 |
b |
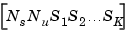 |
c |
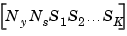 |
d |
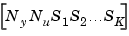 |
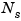 is the maximum of the number of states in each model in the array.
is the maximum of the number of states in each model in the array.
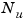 is the number of inputs in each model.
is the number of inputs in each model.
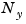 is the number of outputs in each model.
is the number of outputs in each model.
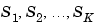 are the lengths of the array dimensions.
are the lengths of the array dimensions.
Specifying Arrays of FRD Models Using frd
To specify a K-dimensional array of p-output, m-input FRD models for which 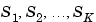 are the lengths of the array dimensions, use
are the lengths of the array dimensions, use
frequency is a real vector of n frequency data points common to all FRD models in the LTI array.
response is a p-by-m-by-n-by-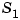 -by-
-by- -by-
-by-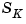 complex-valued multidimensional array.
complex-valued multidimensional array.
units is the optional string specifying 'rad/s' or 'Hz'.
Note that for specifying an LTI array of SISO FRD models, response can also be a multidimensional array of 1-by-n matrices whose remaining dimensions determine the array dimensions of the FRD.
 | Building LTI Arrays Using the stack Function | Indexing Into LTI Arrays |  |