| Design Case Studies |   |
Design Analysis
To analyze this design, form the closed-loop system and plot the closed-loop step response.
This response depends on your closed loop set point. The one shown here is relatively fast and settles in about 0.07 seconds. Therefore, this closed loop disk drive system has a seek time of about 0.07 seconds. This is slow by today's standards, but you also started with a very lightly damped system.
Now look at the robustness of your design. The most common classical robustness criteria are the gain and phase margins. Use the function margin to determine these margins. With output arguments, margin returns the gain and phase margins as well as the corresponding crossover frequencies. Without output argument, margin plots the Bode response and displays the margins graphically.
To compute the margins, first form the unity-feedback open loop by connecting the compensator 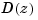 , plant model, and feedback gain
, plant model, and feedback gain 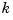 in series.
in series.
Next apply margin to this open-loop model. Type
To obtain the gain margin in dB, type
You can also display the margins graphically by typing
The command produces the plot shown below.
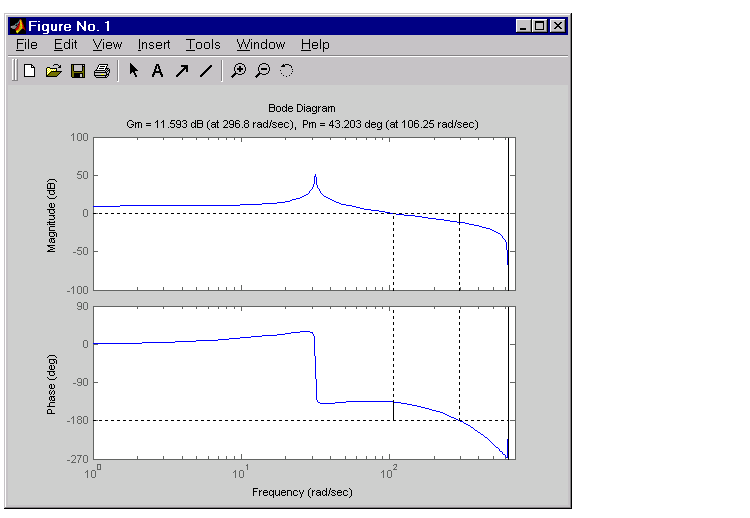
This design is robust and can tolerate a 11 dB gain increase or a 40 degree phase lag in the open-loop system without going unstable. By continuing this design process, you may be able to find a compensator that stabilizes the open-loop system and allows you to reduce the seek time.
 | Adding a Lead Network | LQG Regulation: Rolling Mill Example |  |